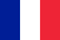
The adenoma of prostate, also called benign hyperplasia of the prostate gland (DGPZ), is an extremely common disease in men over 40 years.With this disease, there is a benign growth of the glandular tissue of the prostate, which can lead to the compression of the urethra, the deteriorated urinary output of the bladder and, as a result, unpleasant sensations during the urine.The adenoma of the prostate can also cause serious problems with the bladder and the kidneys.
This article analyzes the causes and symptoms of prostate adenoma, as well as modern diagnostic and treatment methods of this disease.There are many effective methods to treat benign prostate hyperplasia, including not only pharmacological therapy and open surgical intervention, but also minimally invasive surgical treatment methods.If the first symptoms of the disease appear, you must consult a doctor who takes into account their symptoms, the size of hyperplasia, as well as the general condition of your health and will offer you the best treatment option.
Reasons
To date, it is not entirely clear what kind of reasons lead to an increase in the prostate.However, this may be due to a change in the balance of sex hormones in the male body.Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, male hormone and a small amount of estrogen, female sex hormone.As the body ages, the amount of active testosterone in the blood decreases, while the amount of estrogen remains at approximately at the same level.Studies have shown that the greatest estrogen fraction that enters the prostate gland can increase substances activity that accelerates the growth of prostate cells.
Another theory indicates the role of another male sex hormone (digidrotesterone, which is important for the development and growth of a prostate at a younger age. Some studies have shown that even when the level of testosterone in the blood begins to fall, in the prostate gland there is still a high level of digidrotesterone, which can push the cells of the prostate to continue growing.
The prostate gland is directly under the bladder.The urethra (or urethra), which eliminates the urine from the bladder, passes through the center of the prostate gland.Due to such anatomical structure that a prostate increases it can block urine flow.
The risk factors to increase the prostate gland can be:
- Age.In men under 40, symptoms of an increase in the prostate gland are rarely observed.About 30% of men experience moderate symptoms in 60 years, and approximately 50%, for 80 years.
- The presence of a DGPZ in relatives.If their blood relatives, for example, have a father or brother, have problems with the prostate gland, then this means that the risk of prostate hyperplasia may also have increased.
- Other diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and erectile dysfunction.Studies show that diabetes, erectile dysfunction, as well as heart disease and blood vessels, in some cases can increase the risk of DGPZ.
- Life.Obesity increases the risk of DGPZ, and physical exercises can reduce this risk.
However, the presence of any of the above factors is not the basis to believe that it will definitely develop a prostate adenoma.
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms in different people with prostate adenoma is different.
DGPZH's general signs and symptoms include:
- Frequent or urgent desire to urinate.
- Increased urination at night (Nokturia).
- The inability to empty completely.bladder.
- The presence of residual urine volume in the bladder.
- Weak urine flow or periodic stops during urination.
- The complexity of the start of urine.
- Urine growth at the end of urine.
- Frequent infections of urinary tract.
- The complete impossibility of Oruría (Anuria).
- The presence of blood in the urine (hematuria).
It is worth knowing that the size of the prostate gland does not necessarily determine the seriousness of its symptoms.Some men with a slightly enlarged prostate may have serious symptoms, while other men even with extremely enlarged prostate glands can be insignificant.Almost all patients are characterized by the gradual deterioration of symptoms over time.It is extremely rare that symptoms can stabilize or even improve over time.
Diagnosis
In case of suspicion of DGPZ, your doctor asks detailed questions about the presence of disease symptoms and perform a physical examination.This initial stage may include:
- A survey to identify symptoms and risk factors of the disease.
- Rectal finger exam.To evaluate the size and shape of the prostate gland, the doctor must insert a finger into the rectum.This study is extremely informative, which allows you to draw the main conclusion on the status of the prostate gland.
- Urine analysis.An analysis of the sample of your urine can help eliminate infection or other conditions that can cause similar symptoms.
- Blood test.Blood analysis results may indicate the availability of kidney problems.
- Blood analysis for specific prostate antigen (PSA).The dog is a protein produced only by a prostate fabric.When the prostate is healthy, it is very small dog in the blood.The test can be performed at the Laboratory, Hospital or Medical Office.Special training is not required.The rapid increase in dog level can be a sign that the rapid growth of the prostate fabric occurs.DGPZH is one of the possible causes of a high level of PSA.The inflammation of the prostate, or prostatitis, is another common cause of the high level of the dog.
After performing an initial exam and the necessary tests, your doctor may recommend additional studies to confirm the presence of a DVGPh and exclude other conditions.These tests may include:
- Urodynamic examination.In this study, the patient is urinated in a container attached to a special device, which measures the strength and volume of the current during the urine.The test results help track the dynamics of the development of the disease, determining whether your condition improves or worsens.
- Try the residual urine volume.This test shows if you can completely empty your bladder.The test can be done using an ultrasound study or introducing a catheter in the bladder after it is helping to measure how much urine is in your bladder.
- Maintain a 24 -hour urine diary.The registration of urination and the amount of urine can be especially useful if more than a third of their daily urine is produced at night.
- Transrectal ultrasound.At the same time, the UZ-zond is introduced into the rectum to measure the size and evaluate the status of the prostate.
- Bladder study (cystoscopy).In this study, a flexible catheter is inserted with a camera at the end (cystoscope) in the urethra, which allows the doctor to see the internal surface of the urethra and the bladder.
- Prostate biopsy.It may be necessary to take prostate fabric samples to exclude prostate cancer.
Treatment
There are many different treatment options for prostate adenoma.You and your doctor should decide which treatment suits you.Sometimes, a combination of several procedures works better.Mild cases of DHCH may not need treatment.
The main types of treatment for prostate adenoma are:
- Active observation of the disease.
- Pharmacological therapy.
- Small invasive surgery.
- Surgical interventions.
- Active observation.
If your doctor prefers this option, your disease will be carefully monitored without using any medicine or surgical procedure.At the same time, they will examine it annually.If your symptoms will deteriorate or new symptoms appear, your doctor can offer you an active treatment.Men with light symptoms can be good candidates for active observation.Men with moderate symptoms who do not bother them are also good candidates.
The advantage of this approach is that there are no side effects, but it is likely to reduce symptoms.
Medical therapy
ALFA BLOCATORS
Alpha blockers are medications that relax the muscles of the urethra, the prostate and the bladder.They improve the urine output and reduce DHCH's symptoms, without affecting the size of the prostate.Alfa blockers include alfuzosina, terazozina, doxazosine and tamsulosin.
One of the advantages of alpha blockers is that they start working immediately after admission.Side effects may include dizziness, fatigue and problems with ejaculation.
The moderate to Severo DGPZ men and the men who are concerned about their symptoms are good candidates to begin alpha blockers therapy.
5-INHIBITORS OF THE ALFA REDUCASA
5-Speed 5-Alpha inhibitors are drugs that block the production of dihydrotestosterone, male hormone, which can accumulate in the prostate and cause its growth.These drugs lead to a decrease in the size of the prostate and increase the output of the urine.These medications include Finatoride and Dutteride.
These medications significantly reduce the risk of developing DHCH complications.They also reduce the probability that you need an operation in the future.Side effects include erectile dysfunction and a decrease in libido (impulse sex).At the same time, you will have to continue constantly taking tablets to prevent repeated occurrence of the symptoms of the disease.
Combined therapy
In combined therapy, alpha blockers and inhibitors of the 5 ALFA reductase are used jointly.Possible drug combinations include finsteride and doxasosine or dutterida and tamsulosin.Its urologist can also prescribe a combination of alpha blockers and medications called muscarine receptor blockers if it has symptoms of bladder hyperactivity.With a hyperactive bladder, the bladder muscles are not controlled and cause an increase in the frequency of urine, sudden desires of urinary and urinary incontinence.Antiameascarine medications are drugs that relax the bladder muscles.
Combined therapy significantly improves symptoms and prevents deterioration in the state of DHGPH.However, it is worth remembering that each medicine can cause side effects.Taking two drugs, you can have more side effects than if you take only one drug.
Alternative treatment methods
The auto -medical, the use of traditional medicine or treatment using several herbs (herbal medicine) is not recommended for medical workers.Many studies show that the use of such treatment is not effective and, in some cases, irreparable damage can bring.In addition, herbs and biologically active food additives (dietary supplements) do not pass the same test process as drugs.As a result, the quality and cleaning of the additives sold without a recipe can vary.
Small invasive surgical interventions
The minimally invasive interventions are carried out with minimal anesthesia and suggest a faster recovery.Very often, the procedure can be carried out directly in the doctor's office or an outpatient center.
Instant relief of disease symptoms is the greatest advantage of minimally invasive surgery.In many men, after carrying out a minimally invasive intervention, the urine output and control of the bladder function is improved.If you have problems with urine, the obstruction of the urinary tract, the bladder calculations, the blood in the urine, the presence of the residual urine volume in the bladder after the emptying or did not realize the effect of taking medications, then the minimally invasive intervention can be the next step in the treatment of the disease.
However, it is worth knowing that surgical interventions, including minimally invasive, have a risk of side effects, including:
- Urinary tract infections.
- Blood in the urine.
- Burning during urination.
- The need for a more frequent emptying of the bladder.
- Sudden urine.
- Erectile dysfunction.
Minimally invasive surgery methods include:
- The elevation of a prostate urethra (or Pul Methodology): With this procedure, a special device is used to install small implants in the prostate gland.These implants rise above and maintain a enlarged prostate in this position, while the pressure on the urethra decreases and the urine output improves.In this case, the destruction or elimination of the tissue of the prostate gland is not produced.Pul can be done with local and general anesthesia.Most patients notice an improvement in symptoms within 2 weeks.In some cases, pain or ardor can occur when urinating, blood in the urine or a strong constant desire to urinate.In general, these side effects take place within two to four weeks.Good candidates to carry out an elevation of the prostate urethra can be patients who have a history of other health problems or patients for whom surgical intervention has a high risk.
- Transuretral microwave therapy (or the TUMT method): microwaves are used in this procedure to destroy the prostate tissue.First, the doctor presents a catheter through the urethra to the prostate gland, and then sends microwave integrated into the catheter to heat the selected sections of the prostate.High temperature destroys an excess of prostate fabric.With this procedure, anesthesia is generally required, the risk of side effects is minimal.
- The method of treating prostate pathologies using water vapor convection ablation (rezum therapy): this procedure uses thermal energy to destroy excess prostate tissue.In this case, sterile water inside a special portable device is heated at a temperature just above the boiling point when it becomes steam.This hot steam causes the rapid death of cells.The treatment can be carried out in the doctor's office under local anesthesia.After the procedure, you can have a blood mixture in the urine for some time, you must also use a catheter for several days.Painful or frequent urination after the procedure must pass after approximately 3 weeks.Sex side effects, such as erectile dysfunction, are unlikely.
Traditional surgical operations
Surgical interventions with the elimination of part of the prostate tissue are performed with the inefficiency of other therapy methods, with extremely expressed symptoms (for example, with total impossibility of urine).These include:
- Transureral prostate resection (CUT)
The Trap is one of the most common operations in DHC.During this operation, after performing anesthesia, the surgeon introduces a special thin tool through the head of the penis into the urethra.Using this tool, the doctor eliminates the excessive fabric of the prostate gland.After the procedure, it is generally necessary to use a catheter for 1-2 days.The effect of such treatment generally lasts 15 years or more.Like any other operation, the CURP has side effects and anesthesia used in the intervention, is associated with a certain risk.The side effects of the CURP may include retrograde ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, urinary tract infection after surgery and urinary incontinence.Complete recovery takes 4 to 6 weeks.
- Prostate laser enucleation
With this intervention, the surgeon puts a thin tool through the penis in the urethra.The laser inserted in the tool destroys an excess of prostate fabric.At the same time, as with the transureral resection of the prostate, cuts should not be made.Recovery after laser enucleation is very fast, but after that for several days, it can have a mixture of blood in frequent or painful urine.With this procedure, anesthesia is also required, which is associated with certain risks.
- Prostate elimination operations
Currently, operations to eliminate prostate during DGPZ in men are extremely rare with the inefficiency of all other therapy methods.These operations are associated with significant risks and side effects, including urination, violations of erectile function and serious complications during the operation itself.
Complications
The absence of timely medical care in the DGPG can lead to the development of serious complications, which include:
- Sudden and complete disability to urinate (delayed urine, Anuria).In this state, it may be necessary to enter a catheter in the bladder to provide a urine outlet from a bladder full of people.In some cases, surgery may also be required to reduce urinary retention.
- Urinary tract infections.The inability to completely empty the bladder can increase the risk of infections in the urinary tract.
- The Bladder stones.The bladder stones are also formed due to the impossibility of completely emptying the bladder.The stones can cause the development of infections, irritation of the bladder, blood impurities in the urine and greater difficulties in the output of the urine.
- Damage to the bladder.With the incomplete emptying, the bladder can be stretched, which over time leads to a weakening of its muscle wall.As a result, the bladder becomes unable to compress properly, which becomes the cause of more difficulties in its emptying.
- Kidney damageUrine delay can cause an increase in bladder pressure and the reverse output of the urine to the kidneys, which can cause direct damage or increase the risk of infectious diseases.Such complications are extremely serious and can remain for life.
In most men with an increase in the prostate gland, these complications develop extremely rarely, however, it should be remembered that many complications, including acute urinary retention or damage to the kidneys, can represent a serious threat to their health and life.If any disease symptom occurs, consult a doctor immediately.
Diet and development prevention of prostate adenoma
Unfortunately, there is no reliable way to prevent the development of prostate adenoma, but the rate of increased prostate can lose weight loss and adequate nutrition with a high content of fruits and vegetables in the diet.This may be due to the fact that the excessive amount of adipose tissue in the body can increase the level of hormones and other blood factors and stimulate the growth of prostate cells.Constant physical activity also helps control the weight and level of hormones, thus reducing the risk of developing prostate adenoma.